DAS architecture¶
- DAS architecture is based on several components:
- common core library
- analytics DB
- mapping DB
- caching DB
- merging DB
- logging DB
- data-service plugins, each plugin contains
- data-service handler class
- API map
- notation map
- cache server
- client web server
- common core library
The last two components, cache and client servers, are optional. The code itself can work without cache/client servers with the CLI tool which uses core libraries. But their existence allows the introduction of DAS pre-fetch strategies, DAS robots, which can significantly improve responsiveness of the system and add multi-user support into DAS. The following picture represents current DAS architecture:
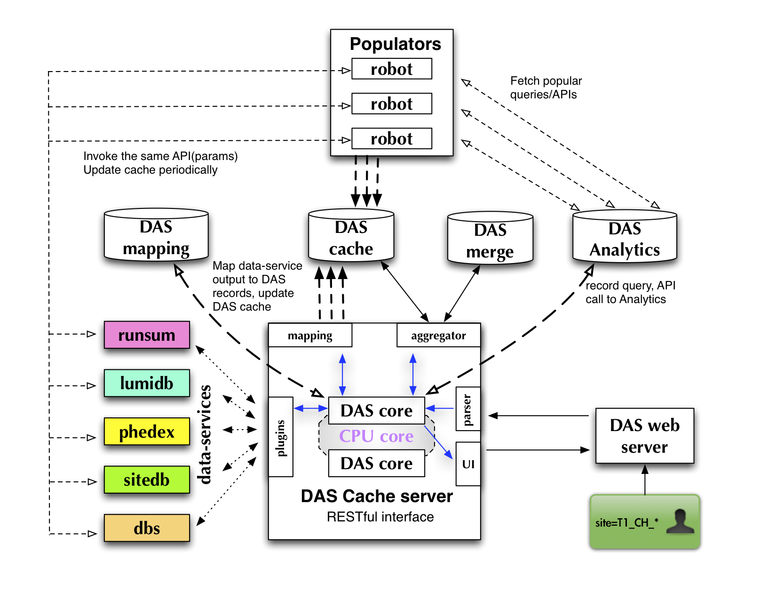
It consists of DAS web server with RESTful interface, DAS cache server, DAS Analytics/Mapping/Cache DBs and DAS robots (for pre-fetching queries). The DAS cache server uses multithreading to consume and work on several user requests at the same time. All queries are written to the DAS Analytics DB. A mapping between data-service and DAS notations is stored in the DAS Mapping DB. Communication with end-users is done via set of REST calls. User can make GET/POST/DELETE requests to fetch or delete data in DAS, respectively. The DAS workflow can be summarised as:
- DAS cache-server receives a query from the client (either DAS web server or DAS CLI)
- The input query is parsed and the selection key(s) and condition(s) identified and mapped to the appropriate data-services
- The query is added to the DAS Analytics DB
- The DAS cache is checked for existing data
- if available
- Data is retrieved from the cache
- otherwise:
- The necessary data services are queried
- The results are parsed, transformed and inserted into the DAS cache
- The user receives a message that the data is being located
- if available
- The data is formatted and returned to the user
For more information please see the DAS workflow page. The DAS DBs use the MongoDB document-oriented database (see [Mongodb]), although during design/evaluation process we considered a number of other technologies, such as different RDMS flavors, memcached [Memcached] and other key-value based data stores (eg CouchDB [Couchdb]), etc.